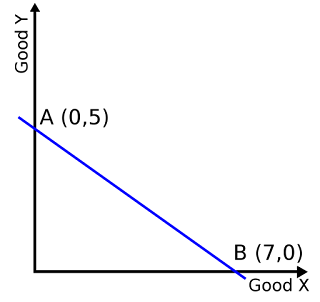
BUDGET CONSTRAINT
Budget constraint refers to all the
combinations of goods and services that a consumer can buy at current prices
within the limits of his or her income. Consumer theory examines the parameters
of consumer choices using the concepts of a budget constraint and a preference
map. In the two-good case, both concepts have ready graphical representations.
The consumer can only buy as much as their income allows, so they are
restricted by their budget. A budget constraint is the total number of items
you can afford within your current budget. A budget constraint illustrates the
range of options available within that budget.
UTILITY
MAXIMIZATION
Utility
maximization refers to the idea that individuals and businesses want to get the
most satisfaction out of their economic decisions. It is also the idea that
consumers and businesses want to get the most out of their purchases in terms
of satisfaction or utility. Utility maximization can also refer to other
decisions, such as the best number of hours for labor to supply. Working more
increases income while decreasing leisure time. In classical economics, utility
maximization is a key concept. It arose as a result of the utilitarian
philosophers Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. Utility maximization was
incorporated into economic theory by early economists such as Alfred Marshall.

Comments
Post a Comment